
To mark our second anniversary, we take a look at so-called gun cotton (nitrocellulose).
- Subject:
- Chemistry
- Physical Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Date Added:
- 10/31/2013

To mark our second anniversary, we take a look at so-called gun cotton (nitrocellulose).

We take a look at one of the most famous acids - Hydrochloric Acid - which is used commonly in labs and found in our stomachs.

We dissolve a goose skull in HCl during the second part of our video about Hydrochloric Acid.

Hafnium is element number 72. This video is one of the 118 clips included in the periodic table of elements themed collection created by Brady Haran and the University of Nottingham in the UK.
Introduction to half-life
Paul Andersen explains how a radioactive nuclei can decay by releasing an alpha, beta, or gamma particle. The exact moment of decay for each nuclei can not be determined but probability is useful in predicting the half-life.
This TED talk by Hans Roslin makes the point that the washing machine was the greatest invention of the Industrial Resolution. The resource, "Hans Rosling: the Magic Washing Machine" included in "Lesson 2 Material Possessions and Sustainability" is a part of "Unit 01 What is Sustainability" included in Energy & Sustainability ES - Course 1.
Paul Andersen explains how the wavelength of a standing wave is determined by the boundary length and frequency of the wave. The fundamental frequency has a wavelength double the boundary length. Harmonics are built on the fundamental frequency.

The Professor once claimed to know nothing about Hassium, but he learned more after visiting Darmstadt in Germany. This video is one of the 118 clips included in the periodic table of elements themed collection created by Brady Haran and the University of Nottingham in the UK.
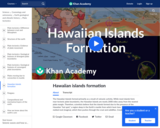
Hawaiian Islands formed by stationary hot spot under Pacific plate

Il y a des femmes qui ont marqué et marquent encore la vie sociale, politique et culturelle d’Haïti : des femmes scientifiques, journalistes, militantes féministes, défenseures des droits humains, politiciennes, écrivaines…
When smoke from wildfires swirls around health care facilities, prepared hospitals in California and Colorado use air quality tools to keep the indoor environment safe for patients and staff.
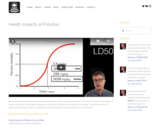
Paul Andersen explains how chemicals can cause both chronic and acute diseases. A discussion of the five main types of toxins; neurotoxins, carcinogens, teratogens, endocrine disruptors, and allergens is including. The LD50 method of determining toxicity as well as a discussion of bioaccumulation and biomagnification is is included.
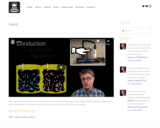
Paul Andersen explains how heat is the movement of energy from an object with a higher temperature to an object with lower temperature. Heat transfer can occur through conduction, convection, and radiation.
In this video Paul Andersen explains how energy can be transferred from warmer objects to colder objects through heat. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. When two objects are in contact collisions between the particles will transfer energy from the warmer object in the form of heat.
Understanding conductive, convective, and radiative heat transfer using a thermal camera.

Students learn the fundamental concepts of heat transfer and heat of reaction. This includes concepts such as physical chemistry, an equation for heat transfer, and a basic understanding of energy and heat transfer.
Students explore heat transfer and energy efficiency using the context of energy efficient houses. They gain a solid understanding of the three types of heat transfer: radiation, convection and conduction, which are explained in detail and related to the real world. They learn about the many ways solar energy is used as a renewable energy source to reduce the emission of greenhouse gasses and operating costs. Students also explore ways in which a device can capitalize on the methods of heat transfer to produce a beneficial result. They are given the tools to calculate the heat transferred between a system and its surroundings.
Heat transfer is an important concept that is a part of everyday life yet often misunderstood by students. In this lesson, students learn the scientific concepts of temperature, heat and the transfer of heat through conduction, convection and radiation. These scientific concepts are illustrated by comparison to magical spells used in the Harry Potter stories.
Paul Andersen explains how heating is the transfer of energy (heat) from a warmer object to a cooler object. Heat can be transferred through conduction, convection and radiation. At the microscopic level conduction results from the collision of particles and therefore the transfer of kinetic energy.