Reconciling with the traditional Drake Equation
- Subject:
- Astronomy
- Physical Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Khan Academy
- Date Added:
- 09/22/2013

Reconciling with the traditional Drake Equation
Taking a shot at estimating the number of detectable civilizations
More reasons why we haven't detected anything yet.
Students use two different methods to determine the densities of a variety of materials and objects. The first method involves direct measurement of the volumes of objects that have simple geometric shapes. The second is the water displacement method, used to determine the volumes of irregularly shaped objects. After the densities are determined, students create x-y scatter graphs of mass versus volume, which reveal that objects with densities less than water (floaters) lie above the graph's diagonal (representing the density of water), and those with densities greater than water (sinkers) lie below the diagonal.
In this deterministic cellular automata model, interactions between neighboring automata are described using a prisoner's dilemma. Limiting dispersal of seeds of annual plants can permit heterogeneous co-existence, whereas thorough mixing instead allows one subpopulation to dominate quickly.

Developing Change Agents examines the role of academia in creating the next generation of sustainability leaders. Delving into strategies to transform higher education, this volume empowers universities to develop change agents who can scale solutions to meet the wicked environmental, social, and political challenges of the present and future. Developing Change Agents advances a revolutionary perspective on the way academia functions from the administrative hierarchies to faculty, and the classroom and to deep engagement in the communities where the solutions must be co-created. This book works to find a transdisciplinary, effective method of tackling the world’s issues with reference to emotional intelligence, diversity, community, and reward structures and supports a tailored, reflexive approach based upon each university’s diverse and unique students, faculty, programs, and communities.
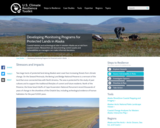
Coastal habitats and archeological sites in western Alaska are at risk from coastal erosion. Researchers are documenting current assets and vulnerabilities so managers can make informed decisions.

It's not easy to keep faucets flowing year-round in southwest Florida. To make sure their customers can get ample clean water at a good priceeven through dry seasonswater utility managers crafted a useful index to help them decide which water sources to use.
The Paleolithic and Neolithic eras of the Stone Age.

Ce dictionnaire a été d’abord pensé pour répondre aux besoins de formation des équipes internationales du projet Yanayi[1], qui vise la co-création d’une base internationale de données ouvertes qualitatives sur les changements climatiques tels que vécus, observés, analysés et combattus par des aînés et des aînées d’Afrique francophone subsaharienne et d’Haïti et racontés à des étudiants et étudiantes affilié-e-s à 10 boutiques des sciences et des savoirs.Cet ambitieux et énorme projet ne pourra avancer que s’il repose sur la collaboration de nombreux participants et nombreuses participantes.Il est possible de : se proposer pour rédiger une entrée qui est encore disponible, c’est-à-dire qui apparaît dans la table des matières du Dictionnaire; proposer une entrée qui est absente du dictionnaire, avec ou sans texte; proposer ses services pour traduire des entrées dans des langues africaines; réviser et compléter une entrée; réviser les références bibliographiques et la qualité linguistique des entrées. L’adresse mail de contact est reseauliraj@gmail.com. Merci d’y envoyer toutes vos questions ou propositions.
In this video, we use direction fields (drawn as quiver plots) to illustrate the numerical integration of differential equations. We include a heuristic example of how one might try to adapt step size by comparing different orders of approximation.
In the first video, we present a biological circuit topology from Ma, Trusina, El-Samad, Lim, and Tang, "Defining network topologies that can achieve biochemical adaptation," Cell, 138: 760-773 (2009). This topology supports adaptation, which is not the absence of change in response to stimulation/stress, but, instead, the ability to produce delayed compensation for those changes. In the second video, we summarize the method of almost linear stability analysis used to solve for the dynamics of this example system.

To describe how oscillations are supported in systems of differential equations, we present a classic "Romeo and Juliet" picture of two-dimensional oscillations, and we analyze how trajectories change as nullclines are arranged at different angles in the phase plane. In addition to models based on traditional systems of differential equations, dynamical systems with time delays and dynamical systems with stochastic fluctuation (i.e. stochastic resonance) can also support oscillations.

In the five parts of this video, we define the derivative and then build a cribsheet of rules for expressing the slopes of simple functions and combinations of functions. These include the power rule, the chain rule, the product and quotient rules, and the rules for differentiating sinusoidal functions.
The first video segment presents a canonical mathematical example from quantitative biology, in which mRNA is transcribed from a gene sequence, and protein is translated from mRNA. The second segment uses eigenvector-eigenvalue analysis to sketch the trajectories of the system in a phase portrait. Finally, the third segment generalizes the linear stability analysis used to study this example.
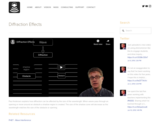
Paul Andersen explains how diffraction can be affected by the size of the wavelength. When waves pass through an opening or move around an obstacle a shadow region is created. The size of the shadow zone will decrease as the wavelength matches the size of the obstacle or opening.

Geographic information systems (GIS), once used predominantly by experts in cartography and computer programming, have become pervasive in everyday business and consumer use. This unit explores GIS in general as a technology about which much more can be learned, and it also explores applications of that technology. Students experience GIS technology through the use of Google Earth on the environmental topic of plastics in the ocean in an area known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. The use of this topic in GIS makes the unit multidisciplinary, incorporating the physics of ocean currents, the chemistry associated with pollutant degradation and chemical sorption to organic-rich plastics, and ecological impact to aquatic biota.
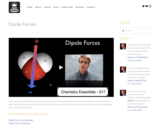
In this video Paul Andersen describes the intermolecular forces associated with dipoles. A dipole is a molecule that has split charge. Dipole may form associations with other dipoles, induced dipoles or ions. An important type of dipole-dipole forces are hydrogen bonds.

Discover Physics is a conceptual physics textbook intended for students in a nonmathematical one-semester general-education course.
With a simple demonstration activity, students are introduced to the concept of friction as a force that impedes motion when two surfaces are in contact. Then, in the Associated Activity (Sliding and Stuttering), they work in teams to use a spring scale to drag an object such as a ceramic coffee cup along a table top or the floor. The spring scale allows them to measure the frictional force that exists between the moving cup and the surface it slides on. By modifying the bottom surface of the cup, students can find out what kinds of surfaces generate more or less friction. They also discover that both static and kinetic friction are involved when an object initially at rest is caused to slide across a surface.