Introduction to the Carnot Cycle and Carnot Heat Engine
- Subject:
- Physical Science
- Physics
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Khan Academy
- Date Added:
- 09/22/2013

Introduction to the Carnot Cycle and Carnot Heat Engine

The "Experiments in Biotechnology" video series is a production of NCCCS BioNetwork in partnership with Haywood and Western Piedmont Community Colleges and features demonstrations of 8 laboratory experiments.
The mechanics of the carry trade

Aquaculture is defined as the farming and husbandry of aquatic organisms. In practice aquaculture or mariculture (saltwater aquaculture) involves commercially growing seafood for consumers. It also involves the sciences of natural resource management and enhancement, collection methods, aquarium technology, facility construction and maintenance, and biotechnology production from marine organisms. Carteret Community College offers the Aquaculture Technology program and emphasizes applied marine sciences and mariculture. The focus of the program is on salt-water species like oysters, clams, soft-shell crabs, and marine finfish like flounder, drum and bait minnows but some freshwater aquaculture species are also covered. Students learn hands-on skills through the Aquaculture Practicum series. Skills such as water quality testing, system construction and maintenance, species collection methods and treatments, feeding and breeding technology are part of the practicums. Students also work with program partners in the industry in practicums and in the cooperative work experience course. Partners include university and government marine sciences laboratories, fishery management agencies, public aquariums, environmental non-governmental organizations, as well as commercial aquatic businesses. The CCC facility is a 5,000 square ft. state-of-the-art showcase for applied marine science, aquatic hatchery and marine biotechnology work. Graduates of the program may find employment on private farms and government hatcheries or at public aquariums. They may also start new businesses in fish, shellfish, or aquatic plant farming, aquatic management services, home/office aquarium or water gardening services. Graduates with the AAS in Aquaculture Technology from CCC can pursue Bachelor's degrees through 2+2 articulations with UNCW and ECU.

Panelist: Phillip (Skip) Kemp Aquaculture is the farming and husbandry of aquatic organisms. Carteret Community College aims to introduce and encourage aquaculture in the region and state as an innovative, practical and economically viable science of applied marine sciences. Topics of Discussion: 1. Farming includes propagation, spawning, culturing of juveniles and production of marketable products. 2. Husbandry includes handling and caring for the organisms during all or a portion of their life cycle. 3. Educational pathways to an aquaculture career. Career choices will be discussed for both aspects of the aquaculture program discussed and extensive footage of the hands-on techniques and training future workers receive will be shown.

The video resource "Cartesian Skepticism - Neo, Meet Rene: Crash Course Philosophy #5" is included in the "Computer Science" course from the resources series of "Crash Course". Crash Course is a educational video series from John and Hank Green.

Carvone is a molecule which comes in two "flavours", spearmint and caraway!
Simple example of cash accounting
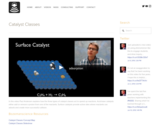
In this video Paul Andersen explains how the three types of catalyst classes act to speed up reactions. Acid-base catalysts either add or remove a proton from one of the reactants. Surface catalysts provide active sites where reactants can adsorb and create more successful collision.
Paul Andersen explains how catalysts can speed up a reaction without being consumed in the reaction. Catalysts can lower the activation energy of reaction be stabilizing the transition state. They can also create new reaction pathways with new reaction intermediates that lower the overall activation energy.
Find out how the flu spreads from person to person, and who is at the greatest risk of getting complications of the flu. Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physician and works at Khan Academy. These videos do not provide medical advice and are for informational purposes only. The videos are not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read or seen in any Khan Academy video.
Paul Andersen discusses cell communication. He begins by explaining how he communicates with other individuals using various forms of electronic communication. He them explains how cells communicate when the distance between them is big, small, and zero. He explains how antigen presenting cells pass information on antigen structure by touching in the immune response.
Paul Andersen explains how the cell cycle is used to create new cells. The creation of identical diploid daughter cells, through mitosis, is described. The creation of unique haploid daughter cells, through meiosis is also described.
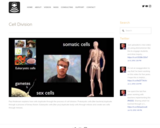
Paul Andersen explains how cells duplicate through the process of cell division. Prokaryotic cells (like bacteria) duplicate through a process of binary fission. Eukaryotic cells (like you) duplicate body cells through mitosis and create sex cells through meiosis.
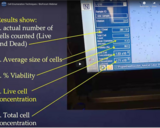
This presentation will discuss different strategies being used today to quantify both plant and mammalian cells for cell culture in the bioprocessing industry or for research.
Paul Andersen gives you a brief introduction to the cell membrane. He starts by describing amphipathic nature of a phospholipid and how it assembles into a membrane. He gives an overview of the fluid mosaic model inside cells. He also discusses the movement of material across a membrane and the role of proteins in movement and function.
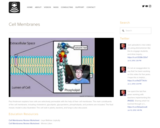
Paul Andersen explains how cells are selectively permeable with the help of their cell membrane. The main constituents of the cell membrane, including cholesterol, glycolipids, glycoproteins, phospholipids, and proteins are included. The fluid mosaic model is also illustrated. The cell wall in plants, bacteria, and fungi is also discussed.
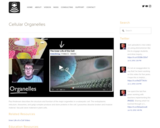
Paul Andersen describes the structure and function of the major organelles in a eukaryotic cell. The endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, and golgi complex produce and store proteins in the cell. Lysosomes dissolve broken and invasive material. Vacuole store material in plant cells.
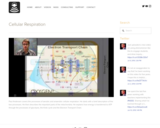
Paul Andersen covers the processes of aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. He starts with a brief description of the two processes. He then describes the important parts of the mitochondria. He explains how energy is transferred to ATP through the processes of glycolysis, the Kreb cycle and the Electron Transport Chain.
Paul Andersen explains how a respirometer can be used to measure the respiration rate in peas, germinating peas and the worm. KOH is used to solidify CO2 produced by a respiring organism.