Stimulate a neuron and monitor what happens. Pause, rewind, and move forward in time in order to observe the ions as they move across the neuron membrane.
- Subject:
- Agriculture & Natural Science
- Biochemistry
- Biology
- Date Added:
- 02/01/2011

Stimulate a neuron and monitor what happens. Pause, rewind, and move forward in time in order to observe the ions as they move across the neuron membrane.
Did you ever imagine that you can use light to move a microscopic plastic bead? Explore the forces on the bead or slow time to see the interaction with the laser's electric field. Use the optical tweezers to manipulate a single strand of DNA and explore the physics of tiny molecular motors. Can you get the DNA completely straight or stop the molecular motor?
Explore stretching just a single strand of DNA using optical tweezers or fluid flow. Experiment with the forces involved and measure the relationship between the stretched DNA length and the force required to keep it stretched. Is DNA more like a rope or like a spring?
What happens when sugar and salt are added to water? Pour in sugar, shake in salt, and evaporate water to see the effects on concentration and conductivity. Zoom in to see how different sugar and salt compounds dissolve. Zoom in again to explore the role of water.

What happens when sugar and salt are added to water? Pour in sugar, shake in salt, and evaporate water to see the effects on concentration and conductivity. Zoom in to see how different sugar and salt compounds dissolve. Zoom in again to explore the role of water.
How do greenhouse gases affect the climate? Explore the atmosphere during the ice age and today. What happens when you add clouds? Change the greenhouse gas concentration and see how the temperature changes. Then compare to the effect of glass panes. Zoom in and see how light interacts with molecules. Do all atmospheric gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?
In this video Paul Andersen explains the major phases of meiosis including: interphase, prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, cytokinesis, interphase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II. He explains how variation is created in the next generation through meiosis and sexual reproduction.
In this video Paul Andersen explains the importance of mitosis and details the major steps in the cell cycle. He explains the importance of Interphase, Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophases, and Cytokinesis.
More detail on the Calvin Cycle and Photorespiration
Hank explains the extremely complex series of reactions whereby plants feed themselves on sunlight, carbon dioxide and water, and also create some by products we're pretty fond of as well.
Paul Andersen explains the process of photosynthesis by which plants and algae can convert carbon dioxide into useable sugar. He begins with a brief description of the chloroplast. He describes the major pigments in a plant (like chlorophyll a and b). He then describes both the light reaction and the Calvin cycle.
Overview of photosynthesis

The video resource "Photosynthesis: Crash Course Biology #8" is included in the "Biology" course from the resources series of "Crash Course". Crash Course is a educational video series from John and Hank Green.
Mr. Andersen shows you how to sink leaf chads in preparation for the AP Biology photosynthesis lab. An empty syringe is used to remove gas from the leaves before the lab. As the chloroplasts absorb light they produce oxygen bubbles which eventually cause the leaves to float.
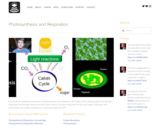
Paul Andersen details the processes of photosynthesis and respiration in this video on free energy capture and storage. Autotrophs use the light reactions and the Calvin cycle to convert energy from the Sun into sugars. Autotrophs and heterotrophs use cellular respiration to convert this sugar into ATP.
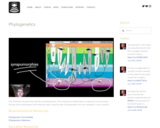
Paul Andersen discusses the specifics of phylogenetics. The evolutionary relationships of organisms are discovered through both morphological and molecular data. A specific type of phylogenetic tree, the cladogram, is also covered.
Hank describes why plants are so freaking amazing - discussing their evolution, and how their cells are both similar to & different from animal cells.

The video resource "Plant Cells: Crash Course Biology #6" is included in the "Biology" course from the resources series of "Crash Course". Crash Course is a educational video series from John and Hank Green.
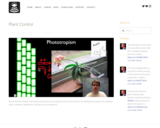
Paul Andersen explains how plants use hormones to respond to their environment. The following hormones are detailed; auxin, cytokinins, gibberelins, abscisic acid and ethylene.

This "Plant Growth, Development, and Response to the Environment" learning object is the from the Sumanas resource series. Sumanas offers a robust selection of content and services that are directed at enhancing the learning experience.