
Animal Diversity Web is a searchable collection of taxonomic and physiological information on many species of animals.
- Subject:
- Agriculture & Natural Science
- Biology
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Date Added:
- 11/12/2010

Animal Diversity Web is a searchable collection of taxonomic and physiological information on many species of animals.
Paul Andersen briefly surveys members of the Domain Animalia. He begins with brief description of the phylogeny of animals. He then describes the characteristics of all animals, heterotrophy, multicellularity, motility and blastula. He describes eight invertebrates and vertebrates.
What is the Antibiotic Apocalypse? What is it all about? And how dangerous is it? The video "The Antibiotic Apocalypse Explained" is a resource included in the Biology topic made available from the Kurzgesagt open educational resource series.
Ape Clarification - that they have no tails
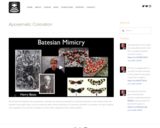
Paul Andersen explains how aposematic coloration (or warning coloration) is used for protection in the natural world. He explains how bright colors can be caused by either sexual selection or a warning coloration to predators. He also explains how organisms can use this coloration to mimic other organisms with a similar pattern.
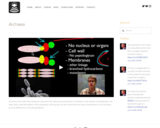
Archaea In this video Paul Andersen describes the defining characteristics of members in the domain archaebacteria. He starts with a brief description of the phylogeny of this group. He then describes the major characteristics on an archaea, such as differences in the phospholipids.
This article discusses how nanotechnology is being used in biomedical research, disease diagnosis, and therapy. The resource, ''Less is More in Medicine Reading Link'' included in "Lesson 2 Cell Physiology" is a part of "Unit 03 Cells and Tissues" included in Health & Life Sciences HLS - Course 1.
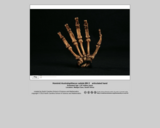
360-degree animation of Australopithecus sebida MH 2 articulated hand
BI 101 is an introductory lab science course intended for majors in disciplines other than the biological sciences. This course is designed to help you discover the applications of science to your everyday life, as well as provide elements of critical thinking. This course has four Credit Units that emphasize a variety of topics including ecological principles, biodiversity, and impact of human activities on the environment.
Course Outcomes:
1. Discuss biological community interactions.
2. Explain how changes in human population and/or actions impact natural ecosystems.
3. Describe the movement of energy & nutrients through trophic levels.
4. Recognize the appropriate taxonomic level of an organism based on key characteristics or traits.
This is an introductory lab science course intended for majors in disciplines other than the biological sciences. The topics presented include biological molecules, cellular biology, genetics and inheritance, biotechnology, and evolutionary processes. Additionally, the course is designed to help you discover the applications of science in your everyday life, as well as provide elements of critical thinking.
Course Outcomes:
1. Explain how natural selection drives evolution.
2. Express how changes in the genome can affect the phenotype or traits within a population.
3. Be able to describe the patterns of inheritance.
4. Be able describe selected key cell processes.
5. Distinguish between the groups of biomolecules.

Reading list for BI 112 with links to OpenStax Human Biology by Willy Cushwa,
OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology,OpenStax Biology 2e, and OpenStax Chemistry: Atoms First.
This textbook is a collection of technology guides to help students understand the technical aspects of bioinformatics.

Backyard Nature contains information about ecology, plants, geology, animals, and more. The site places the investigation of these topics in a typical backyard setting.
Life oPaul Andersen describes the defining characteristics of the domain Eubacteria. He begins with a quick description of the phylogeny of bacteria and horizontal gene transfer. He then surveys the structures of a bacteria; nucleoid region, capsule, pilli, cell wall with peptidoglycan, flagella.
Introduction to bacteria
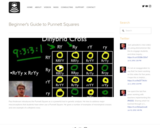
Paul Andersen introduces the Punnett Square as a a powerful tool in genetic analysis. He tries to address major misconceptions that students have when use a Punnett Square. He gives a number of examples of monohybrid crosses and one example of a dihybrid cross.
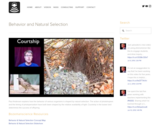
Paul Andersen explains how the behavior of various organisms is shaped by natural selection. The action of phototropism and the timing of photoperiodism have both been shaped by the relative availability of light. Courtship in the bower bird determines the success of offspring.
Hank tells us the story of the complicated chemical dance that allows our skeletal muscles to contract and relax.

The video resource "Big Guns: The Muscular System - CrashCourse Biology #31" is included in the "Biology" course from the resources series of "Crash Course". Crash Course is a educational video series from John and Hank Green.

Students act as if they are biological engineers following the steps of the engineering design process to design and create protein models to replace the defective proteins in a child’s body. Jumping off from a basic understanding of DNA and its transcription and translation processes, students learn about the many different proteins types and what happens if protein mutations occur. Then they focus on structural, transport and defense proteins during three challenges posed by the R&D; bio-engineering hypothetical scenario. Using common classroom supplies such as paper, tape and craft sticks, student pairs design, sketch, build, test and improve their own protein models to meet specific functional requirements: to strengthen bones (collagen), to capture oxygen molecules (hemoglobin) and to capture bacteria (antibody). By designing and testing physical models to accomplish certain functional requirements, students come to understand the relationship between protein structure and function. They graph and analyze the class data, then share and compare results across all teams to determine which models were the most successful. Includes a quiz, three worksheets and a reference sheet.