In this well-illustrated object, learners examine basic floral anatomy. The flower is the reproductive organ of the angiosperm.
- Subject:
- Agriculture & Natural Science
- Biology
- Date Added:
- 10/15/2010

In this well-illustrated object, learners examine basic floral anatomy. The flower is the reproductive organ of the angiosperm.
Learners test their knowledge of fungal diseases by completing six exercises.

Learners view video clips demonstrating Gram's staining procedure. Correctly stained slides are shown.
Learners read how microbes in such items as yogurt, bread, insulin, and insect sprays improve our lives.
The student categorizes defense mechanisms as specific or non-specific.
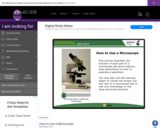
Learners examine the function of each part of a microscope and follow step-by-step instructions on how to focus on a specimen. They also review the proper use and care of a microscope and test their knowledge in two drag-and-drop exercises.
The learner uses observations to diagnose fungal diseases.
Students observe information and formulate an evaluation that includes diagnosis and microorganism identification.
In this interactive object, learners review the case of a patient with meningococcal meningitis.
Students make observations and formulate an evaluation including diagnosis and microorganism identification.
Students make observations and formulate an evaluation that includes diagnosis and microorganism identification and treatment.
Students make observations and formulate an evaluation that includes diagnosis, microorganism identification, and treatment.
The student observes the growth of gram negative organisms that are lactose positive or negative.
Learners read a general description of the function and structure of leaves and examine drawings and microscopic views. A matching exercise completes the learning object.
In this animated activity, sexual reproduction in animals is contrasted with the alternation of generation lifecycle of plants.
In this overview, students examine and identify mannitol positive and mannitol negative bacteria on mannitol salt agar.
In this interactive object, learners categorize different metabolic activities as catabolic or anabolic and follow a glucose molecule through the processes of glycolysis, aerobic respiration, and fermentation.
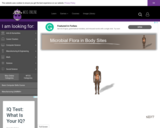
In an interactive exercise, learners identify the human body sites that harbor a normal resident flora and the sites that are sterile.
Learners match the names of parasitic organisms to the diseases they cause and the modes of transmission.
Learners listen to the pronunciation of bacteria names and then type the words. They may choose the number of names that they wish to spell (up to 70). Immediate feedback is given, and a final score is provided at the end of the activity.