How does a basketball apply a force to the shooter's hand?
- Subject:
- Agriculture & Natural Science
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 09/22/2013

How does a basketball apply a force to the shooter's hand?
Learn how Dr. Korotkoff cleverly used a stethoscope to determine blood pressure, and that we still use his trick today! Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physician and works at Khan Academy.
In this video Paul Andersen describes the lipids (of the fats). He explains how they are an important source of energy but are also required to cell membranes. He explains how the hydrocarbon tails in triglycerides contain energy available for life. He also explains how phospholipids construct, and cholesterol molecules main the cell membrane.
Figure out the difference between "salt" and "sodium" and how much salt is recommended on a low sodium diet. Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physician and works at Khan Academy.
Ever wonder why the heart sounds the way that it does? Opening and closing of heart valves makes the heart rhythm come alive with its lub dub beats... Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physician and works at Khan Academy.
Learn about how the flu vaccine is made every year and how they name the strains that they put inside. Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physician and works at Khan Academy.
Sal talks with Professor Laurence Baker of Stanford Medical School
Learn how the needs of the fetus are met by the placenta, which is a special organ that belongs to both the mother and the fetus! Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physician and works at Khan Academy.
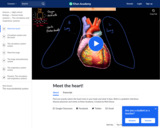
Find out exactly where the heart rests in your body and what it does. Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physician and works at Khan Academy.
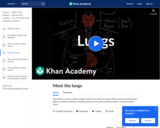
Every time you take a breath, oxygen makes it way into your lungs. Follow along on that journey! Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physician and works at Khan Academy.
Paul Andersen describes the macromolecules that make up living organisms. He starts with a brief description of organic chemistry and the importance of functional groups. He also covers both dehydration and hydrolysis in polymerization. He finally covers the four major macromolecules: nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and carbohydrates.
Learn how to use a Punnett square to solve a Mendelian monohybrid cross with one of the Amoeba Sister's favorite classroom pets: hairless guinea pigs. This v...
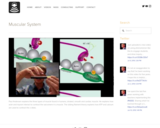
Paul Andersen explains the three types of muscle found in humans; striated, smooth and cardiac muscle. He explains how actin and myosin interact to contract the sarcomere in a muscle. The sliding filament theory explains how ATP and calcium are used to contract the z disks.

In this survey text, directed at those not majoring in biology, we dispel the assumption that a little learning is a dangerous thing. We hope that by skimming the surface of a very deep subject, biology, we may inspire you to drink more deeply and make more informed choices relating to your health, the environment, politics, and the greatest subject that are all of us are entwined in, life itself.
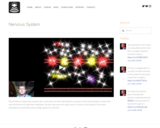
Paul Andersen begins this podcast with a discussion of brain lateralization and gives a brief demonstration of tests that were performed on split-brain individuals. He then discusses the major parts of a neuron and explains how action potentials are generated using voltage-gated ion channels.

http://armandoh.org/Talks about the space between a neuron and muscle, and describes with a bit of detail about this relationship.https://www.facebook.com/Ar...
Neuroscience: Canadian 2nd Edition Open Textbook is a comprehensive source that examines the nervous system, neurodegeneration, techniques in studying neuroscience and emerging topics in the field.
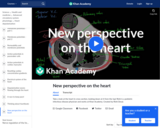
Take a look at the heart in cross section, looking down at it from the top! Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physician and works at Khan Academy.
Dr. Andy Connolly from Stanford Medical School introduces Sal to what normal colon tissue looks like
Paul Andersen explains the importance and structure of nucleic acids. He begins with an introduction to DNA and RNA. He then describes the important parts of a nucleotide and shows how they are connected through covalent and hydrogen bonding.